Publications

The locus coeruleus, a blue spot for early diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer’s disease
Intact functioning of the locus coeruleus-noradrenergic (LC-NA) system is pivotal in the control of numerous central processes, and damage to these systems leads to a wide range of nervous system disorders. The LC, as the main source of noradrenaline (NA) in the mammalian brain, was the first central nervous system (CNS) modulatory structure to be anatomically and biochemically characterized. LC-NA release exerts both excitatory and inhibitory effects on target areas. Over the past few decades, LC damage has been causatively identified as a common factor in CNS diseases, notably neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, LC damage is the likely manifestation of common pathophysiological processes, thus elevating the LC as a diagnostic and therapeutic target, especially in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases (PD & AD). This review also addresses why LC neurons, compared to other areas in particular, are highly vulnerable and sensitive to damage—such as specific anatomical features, tau phosphorylation, and high neuronal energy requirements—will be described in this review article. Finally, we explore whether these known LC vulnerabilities might be leveraged towards improved early diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for AD.

Molecular Logic of Cell Diversity and Circuit Connectivity in the REM Sleep Hub
The complexity of the brain arises from the diversity of its circuits and the molecular heterogeneity of the cells that compose them. A mechanistic understanding therefore requires mapping cellular identity and connectivity at single-cell resolution. Here we define the cellular taxonomy of the murine sublaterodorsal tegmental nucleus (SLD), a critical hub for REM sleep, using single-nucleus RNA sequencing. We identified all major brain cell classes, with oligodendrocytes as the most abundant, and resolved seventeen transcriptionally distinct neuronal groups defined by neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and neuropeptides, each with unique molecular signatures. Projection-specific analysis further revealed that glutamatergic subpopulations targeting the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) and ventral medulla are molecularly distinct, marked by characteristic receptor motifs. Strikingly, we provide the first direct evidence that SLDGLUT neurons innervate the vlPAG. This newly uncovered SLDGLUT→vlPAG pathway represents a previously unrecognized circuit node for REM sleep regulation, with the potential to act as a REM-OFF population suppressing it. Together, these findings establish a transcriptionally resolved atlas of the SLD, reveal the molecular logic of its circuit connectivity, and nominate candidate molecular actuators of REM sleep control, opening new avenues for dissecting how brainstem circuits orchestrate REM state and its transitions.

Suprachiasmatic Neuromedin-S Neurons Regulate Arousal
Mammalian circadian rhythms, which orchestrate the daily temporal structure of biological processes, including the sleep-wake cycle, are primarily regulated by the circadian clock in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). The SCN clock is also implicated in providing an arousal ‘signal,’ particularly during the wake-maintenance zone (WMZ) of our biological day, essential for sustaining normal levels of wakefulness in the presence of mounting sleep pressure. Here we identify a role for SCN Neuromedin-S (SCNNMS) neurons in regulating the level of arousal, especially during the WMZ. We used chemogenetic and optogenetic methods to activate SCNNMS neurons in vivo, which potently drove wakefulness. Fiber photometry confirmed the wake-active profile of SCNNM neurons. Genetically ablating SCNNMS neurons disrupted the sleep-wake cycle, reducing wakefulness during the dark period and abolished the circadian rhythm of body temperature. SCNNMS neurons target the dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus (DMH), and photostimulation of their terminals within the DMH rapidly produces arousal from sleep. Pre-synaptic inputs to SCNNMS neurons were also identified, including regions known to influence SCN clock regulation. Unexpectedly, we discovered strong input from the preoptic area (POA), which itself receives substantial inhibitory input from the DMH, forming a possible arousal-promoting circuit (SCN->DMH->POA->SCN). Finally, we analyzed the transcriptional profile of SCNNMS neurons via single-nuclei RNA-Seq, revealing three distinct subtypes. Our findings link molecularly-defined SCN neurons to sleep-wake patterns, body temperature rhythms, and arousal control.

Enriched experience increases reciprocal synaptic connectivity and coding sparsity in higher-order cortex
The integration of new information during sleep reshapes cortical representations that support categorical knowledge. Auto-associative attractor network theories predict that reciprocal excitatory connections help form stable categorical attractors, but direct evidence is missing. We tested this using ten weeks of enriched experience (ENR) in mice as a model for knowledge accumulation and recorded single-unit activity across hippocampus and neocortex. ENR induced significant remodeling in high- but not low-level neocortex, with a shift from unidirectional to bidirectional excitatory-excitatory connections, suggestive of increased ‘cell assemblies’. This was accompanied by increased inhibitory-to-excitatory connections and sparser, more orthogonal population activity during awake rest and slow-wave sleep, particularly in deep layers. Thus, ENR reorganizes cortical circuits into a symmetric, inhibition-balanced network that improves coding efficiency, supporting long-standing attractor network predictions.

Chronic chemogenetic slow-wave-sleep enhancement in mice
While epidemiological associations and brief studies of sleep effects in human disease have been conducted, rigorous long-term studies of sleep manipulations and in animal models are needed to establish causation and to understand mechanisms. We have previously developed a mouse model of acute slow-wave-sleep (SWS) enhancement using chemogenetic activation of parafacial zone GABAergic neurons (PZGABA) in the parvicellular reticular formation of the pontine brainstem. However, it was unknown if SWS could be enhanced chronically in this model.
In the present study, mice expressing the chemogenetic receptor hM3Dq in PZGABA were administered daily with one of three chemogenetic ligands, clozapine N-oxide (CNO), deschloroclozapine (DCZ) and compound 21 (C21), and sleep-wake phenotypes were analyzed using electroencephalogram (EEG) and electromyogram (EMG).
We found that SWS time is increased for three hours, and at the same magnitude for at least six months. This phenotype is associated with an increase of slow wave activity (SWA) of similar magnitude throughout the 6-month dosing period. Interestingly, at the end of the 6-month dosing period, SWA remains increased for at least a week.
This study validates a mouse model of chronic SWS enhancement that will allow mechanistic investigations into how SWS promotes physiological function and prevents diseases. The approach of a rotating schedule of three chemogenetic ligands may be broadly applicable in chemogenetic studies that require chronic administration.
GABAergic signalling in the suprachiasmatic nucleus is required for coherent circadian rhythmicity
The suprachiasmatic nucleus is the circadian pacemaker of the mammalian brain. Suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons display synchronization of their firing frequency on a circadian timescale, which is required for the pacemaker function of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. However, the mechanisms by which suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons remain synchronized in vivo are poorly understood, although synaptic communication is considered indispensable. Suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons contain the neurotransmitter GABA and express GABA receptors. This has inspired the hypothesis that GABA signalling may play a central role in network synchronization, although this remains untested in vivo. Here, using local genetic deletion, we show that disruption of GABA synaptic transmission within the suprachiasmatic nucleus of adult mice results in the eventual deterioration of physiological and behavioural rhythmicity in vivo and concomitant cellular desynchrony in vitro. These findings suggest that intercellular GABA signalling is essential for behavioural rhythmicity and cellular synchrony of the suprachiasmatic nucleus neural network.
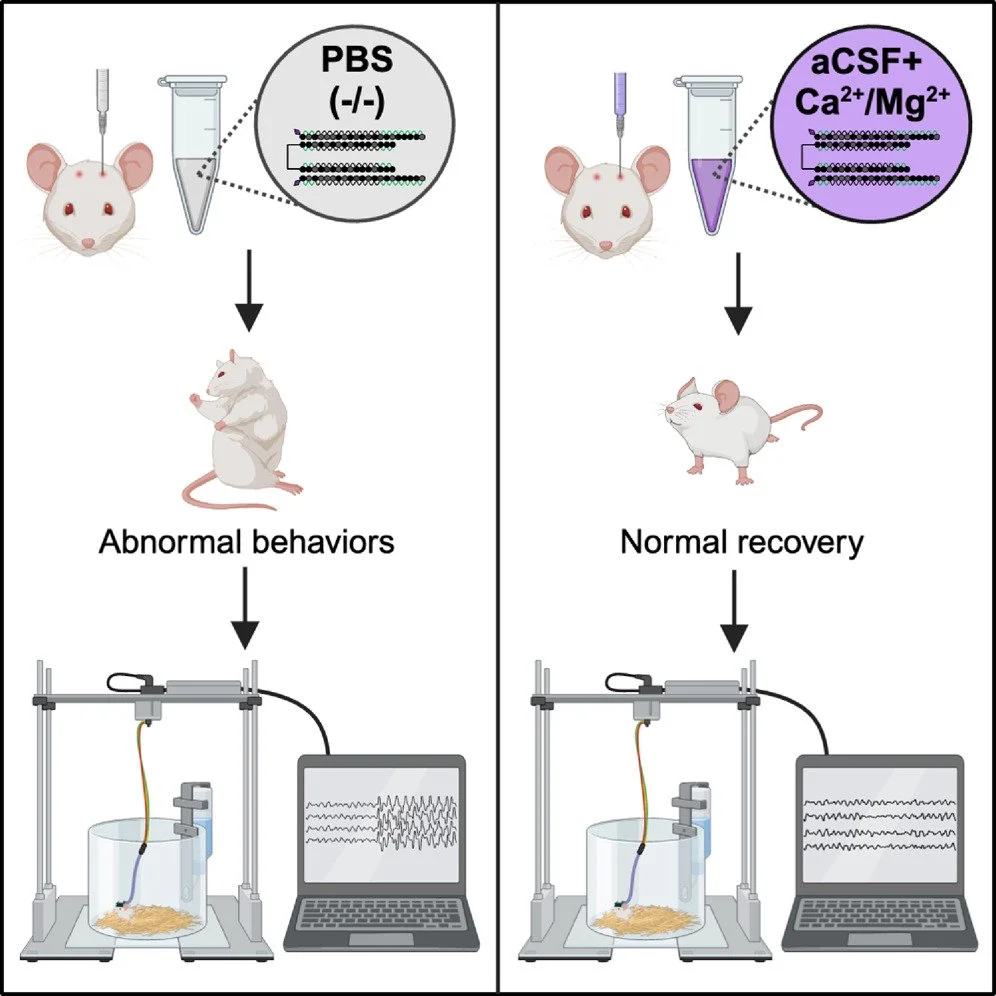
Preventing acute neurotoxicity of CNS therapeutic oligonucleotides with the addition of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the formulation
Oligonucleotide therapeutics (ASOs and siRNAs) have been explored for modulation of gene expression in the central nervous system (CNS), with several drugs approved and many in clinical evaluation. Administration of highly concentrated oligonucleotides to the CNS can induce acute neurotoxicity. We demonstrate that delivery of concentrated oligonucleotides to the CSF in awake mice induces acute toxicity, observable within seconds of injection. Electroencephalography and electromyography in awake mice demonstrated seizures. Using ion chromatography, we show that siRNAs can tightly bind Ca2+ and Mg2+ up to molar equivalents of the phosphodiester/phosphorothioate bonds independently of the structure or phosphorothioate content. Optimization of the formulation by adding high concentrations (above biological levels) of divalent cations (Ca2+ alone, Mg2+ alone, or Ca2+ and Mg2+) prevents seizures with no impact on the distribution or efficacy of the oligonucleotide. The data here establish the importance of adding Ca2+ and Mg2+ to the formulation for the safety of CNS administration of therapeutic oligonucleotides.
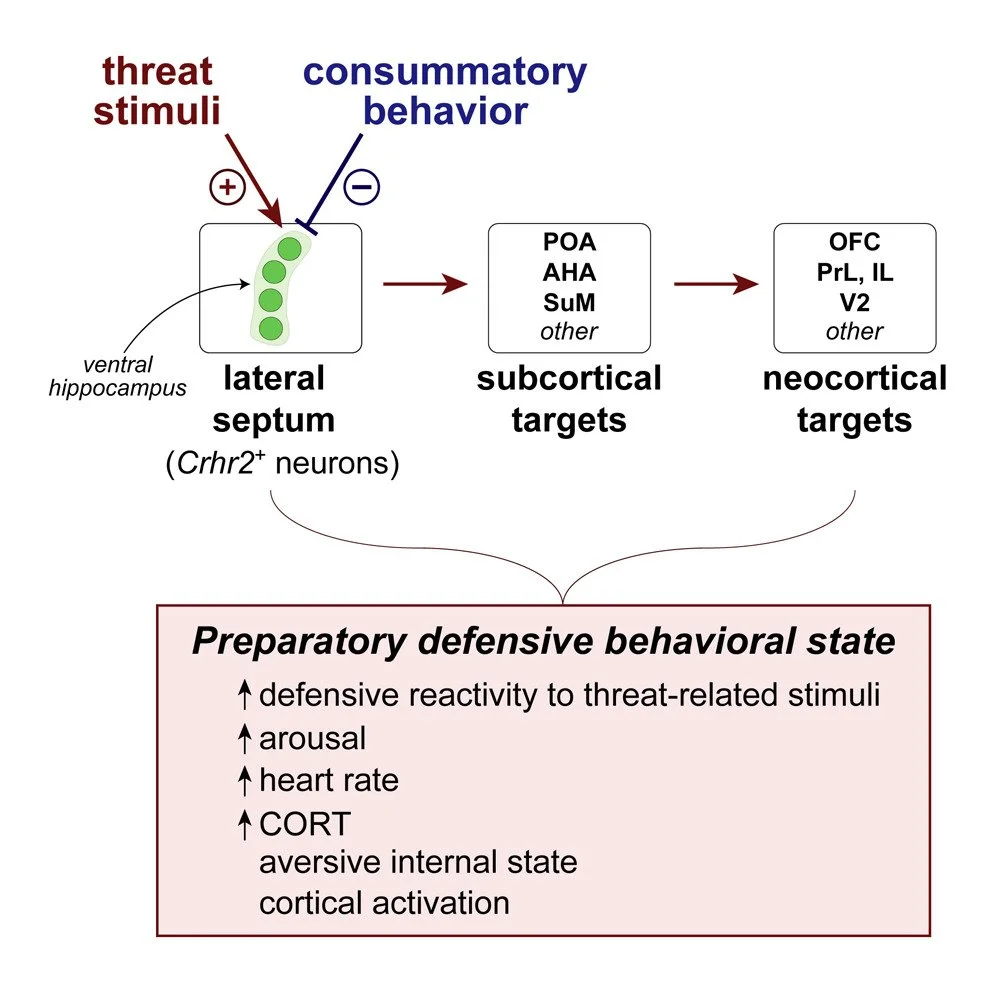
Lateral septum modulates cortical state to tune responsivity to threat stimuli
Sudden unexpected environmental changes capture attention and, when perceived as potentially dangerous, evoke defensive behavioral states. Perturbations of the lateral septum (LS) can produce extreme hyperdefensiveness even to innocuous stimuli, but how this structure influences stimulus-evoked defensive responses and threat perception remains unclear. Here, we show that Crhr2-expressing neurons in mouse LS exhibit phasic activation upon detection of threatening but not rewarding stimuli. Threat-stimulus-driven activity predicts the probability but not vigor or type of defensive behavior evoked. Although necessary for and sufficient to potentiate stimulus-triggered defensive responses, LSCrhr2 neurons do not promote specific behaviors. Rather, their stimulation elicits negative valence and physiological arousal. Moreover, LSCrhr2 activity tracks brain state fluctuations and drives cortical activation and rapid awakening in the absence of threat. Together, our findings suggest that LS directs bottom-up modulation of cortical function to evoke preparatory defensive internal states and selectively enhance responsivity to threat-related stimuli.

Addicted to dreaming
How human brains regulate sleep remains an enduring puzzle (1). How sleep subserves human dreaming—rapid eye movement (REM) sleep—is especially puzzling. There is considerable mechanistic understanding of the synaptic, cellular, and circuit bases of REM sleep (2, 3). However, despite pharmacological evidence that dopamine (DA) can potently modulate REM sleep, this neurotransmitter is conspicuously absent from most prevailing REM sleep circuit models.

Lateral septum modulates cortical state to tune responsivity to threat stimuli
Sudden unexpected environmental changes capture attention and, when perceived as potentially dangerous, evoke defensive behavioral states. Perturbations of the lateral septum (LS) can produce extreme hyperdefensiveness even to innocuous stimuli, but how this structure influences stimulus-evoked defensive responses and threat perception remains unclear. Here, we show that Crhr2-expressing neurons in mouse LS exhibit phasic activation upon detection of threatening but not rewarding stimuli. Threat-stimulus-driven activity predicts the probability but not vigor or type of defensive behavior evoked. Although necessary for and sufficient to potentiate stimulus-triggered defensive responses, LSCrhr2 neurons do not promote specific behaviors. Rather, their stimulation elicits negative valence and physiological arousal. Moreover, LSCrhr2 activity tracks brain state fluctuations and drives cortical activation and rapid awakening in the absence of threat. Together, our findings suggest that LS directs bottom-up modulation of cortical function to evoke preparatory defensive internal states and selectively enhance responsivity to threat-related stimuli.

Validation of DREADD agonists and administration route in a murine model of sleep enhancement
Chemogenetics is a powerful tool to study the role of specific neuronal populations in physiology and diseases. Of particular interest, in mice, acute and specific activation of parafacial zone (PZ) GABAergic neurons expressing the Designer Receptors Activated by Designer Drugs (DREADD) hM3Dq (PZGABA-hM3Dq) enhances slow-wave-sleep (SWS), and this effect lasts for up to 6 h, allowing prolonged and detailed study of SWS. However, the most widely used DREADDs ligand, clozapine N-oxide (CNO), is metabolized into clozapine which has the potential of inducing non-specific effects. In addition, CNO is usually injected intraperitoneally (IP) in mice, limiting the number and frequency of repeated administration.

Elevated TNF-α Leads to Neural Circuit Instability in the Absence of Interferon Regulatory Factor 8
Interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) is a transcription factor necessary for the maturation of microglia, as well as other peripheral immune cells. It also regulates the transition of microglia and other immune cells to a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Irf8 is also a known risk gene for multiple sclerosis and lupus, and it has recently been shown to be downregulated in schizophrenia. While most studies have focused on IRF8-dependent regulation of immune cell function, little is known about how it impacts neural circuits. Here, we show by RNAseq from Irf8−/− male and female mouse brains that several genes involved in regulation of neural activity are dysregulated. We then show that these molecular changes are reflected in heightened neural excitability and a profound increase in susceptibility to lethal seizures in male and female Irf8−/− mice. Finally, we identify that TNF-α is elevated specifically in microglia in the CNS, and genetic or acute pharmacological blockade of TNF-α in the Irf8−/− CNS rescued the seizure phenotype. These results provide important insights into the consequences of IRF8 signaling and TNF-α on neural circuits. Our data further suggest that neuronal function is impacted by loss of IRF8, a factor involved in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases.

Orexin neurons inhibit sleep to promote arousal
Humans and animals lacking orexin neurons exhibit daytime sleepiness, sleep attacks, and state instability. While the circuit basis by which orexin neurons contribute to consolidated wakefulness remains unclear, existing models posit that orexin neurons provide their wake-stabilizing influence by exerting excitatory tone on other brain arousal nodes. Here we show using in vivo optogenetics, in vitro optogenetic-based circuit mapping, and single-cell transcriptomics that orexin neurons also contribute to arousal maintenance through indirect inhibition of sleep-promoting neurons of the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus. Activation of this subcortical circuit rapidly drives wakefulness from sleep by differentially modulating the activity of ventrolateral preoptic neurons. We further identify and characterize a feedforward circuit through which orexin (and co-released glutamate) acts to indirectly target and inhibit sleep-promoting ventrolateral preoptic neurons to produce arousal. This revealed circuitry provides an alternate framework for understanding how orexin neurons contribute to the maintenance of consolidated wakefulness and stabilize behavioral state.

Two novel mouse models of slow-wave-sleep enhancement in aging and Alzheimer’s disease
Aging and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are both associated with reduced quantity and quality of the deepest stage of sleep, called slow-wave-sleep (SWS). Slow-wave-sleep deficits have been shown to worsen AD symptoms and prevent healthy aging. However, the mechanism remains poorly understood due to the lack of animal models in which SWS can be specifically manipulated. Notably, a mouse model of SWS enhancement has been recently developed in adult mice. As a prelude to studies assessing the impact of SWS enhancement on aging and neurodegeneration, we first asked whether SWS can be enhanced in animal models of aging and AD.
The chemogenetic receptor hM3Dq was conditionally expressed in GABAergic neurons of the parafacial zone of aged mice and AD (APP/PS1) mouse model. Sleep–wake phenotypes were analyzed in baseline condition and following clozapine-N-oxide (CNO) and vehicle injections. Both aged and AD mice display deficits in sleep quality, characterized by decreased slow wave activity. Both aged and AD mice show SWS enhancement following CNO injection, characterized by a shorter SWS latency, increased SWS amount and consolidation, and enhanced slow wave activity, compared with vehicle injection. Importantly, the SWS enhancement phenotypes in aged and APP/PS1 model mice are comparable to those seen in adult and littermate wild-type mice, respectively. These mouse models will allow investigation of the role of SWS in aging and AD, using, for the first time, gain-of SWS experiments.

The Sleep-Promoting Ventrolateral Preoptic Nucleus: What Have We Learned over the Past 25 Years?
For over a century, the role of the preoptic hypothalamus and adjacent basal forebrain in sleep–wake regulation has been recognized. However, for years, the identity and location of sleep- and wake-promoting neurons in this region remained largely unresolved. Twenty-five years ago, Saper and colleagues uncovered a small collection of sleep-active neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO) of the preoptic hypothalamus, and since this seminal discovery the VLPO has been intensively investigated by labs around the world, including our own. Herein, we first review the history of the preoptic area, with an emphasis on the VLPO in sleep–wake control. We then attempt to synthesize our current understanding of the circuit, cellular and synaptic bases by which the VLPO both regulates and is itself regulated, in order to exert a powerful control over behavioral state, as well as examining data suggesting an involvement of the VLPO in other physiological processes.

A marked enhancement of a BLOC-1 gene, pallidin, associated with somnolent mouse models deficient in histamine transmission
Histamine and orexin (or hypocretin) neurons act distinctly and synergistically in wake control. A double knockout mouse genotype lacking both histamine and orexins shows all sleep disorders of human narcolepsy. We identified in this mouse brain a sharp upregulation of a BLOC-1 gene, pallidin, that is selectively associated with a deficient histamine neurotransmission and dramatic changes in the balance of cholinergic and aminergic systems in mice as well as an enhanced sleep in drosophila. This study demonstrates potential sleep disorders-associated compensatory mechanisms with pallidin as a novel biomarker.

The Role of the Central Histaminergic System in Behavioral State Control
Histamine is a small monoamine signaling molecule that plays a role in many peripheral and central physiological processes, including the regulation of wakefulness. The tuberomammillary nucleus is the sole neuronal source of histamine in the brain, and histamine neurons are thought to promote wakefulness and vigilance maintenance – under certain environmental and/or behavioral contexts – through their diffuse innervation of the cortex and other wake-promoting brain circuits. Histamine neurons also contain a number of other putative neurotransmitters, although the functional role of these co-transmitters remains incompletely understood. Within the brain histamine operates through three receptor subtypes that are located on pre- and post-synaptic membranes. Some histamine receptors exhibit constitutive activity, and hence exist in an activated state even in the absence of histamine. Newer medications used to reduce sleepiness in narcolepsy patients in fact enhance histamine signaling by blunting the constitutive activity of these histamine receptors. In this chapter, we provide an overview of the central histamine system with an emphasis on its role in behavioral state regulation and how drugs targeting histamine receptors are used clinically to treat a wide range of sleep-wake disorders.

Depleting hypothalamic somatostatinergic neurons recapitulates diabetic phenotypes in mouse brain, bone marrow, adipose and retina
Hypothalamic inflammation and sympathetic nervous system hyperactivity are hallmark features of the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Hypothalamic inflammation may aggravate metabolic and immunological pathologies due to extensive sympathetic activation of peripheral tissues. Loss of somatostatinergic (SST) neurons may contribute to enhanced hypothalamic inflammation.

Carbon Monoxide: from Poison to Clinical Trials
Every cell has a highly sophisticated system for regulating heme levels, which is particularly important with regard to turnover. Heme degradation generates CO and while CO has long been viewed as a metabolic waste product, and at higher concentrations cellularly lethal, we now know that CO is an indispensable gasotransmitter that participates in fundamental physiological processes necessary for survival. Irrefutable preclinical data have resulted in concerted efforts to develop CO as a safe and effective therapeutic agent, but against this notion lies dogma that CO is a poison, especially to the brain. The emergence of this debate is discussed here highlighting the neuroprotective properties of CO through its role on the central circadian clock and ongoing strategies being developed for CO administration for clinical use.

Suprachiasmatic VIP neurons are required for normal circadian rhythmicity and comprised of molecularly distinct subpopulations
The hypothalamic suprachiasmatic (SCN) clock contains several neurochemically defined cell groups that contribute to the genesis of circadian rhythms. Using cell-specific and genetically targeted approaches we have confirmed an indispensable role for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-expressing SCN (SCNVIP) neurons, including their molecular clock, in generating the mammalian locomotor activity (LMA) circadian rhythm. Optogenetic-assisted circuit mapping revealed functional, di-synaptic connectivity between SCNVIP neurons and dorsomedial hypothalamic neurons, providing a circuit substrate by which SCNVIP neurons may regulate LMA rhythms. In vivo photometry revealed that while SCNVIP neurons are acutely responsive to light, their activity is otherwise behavioral state invariant. Single-nuclei RNA-sequencing revealed that SCNVIP neurons comprise two transcriptionally distinct subtypes, including putative pacemaker and non-pacemaker populations. Altogether, our work establishes necessity of SCNVIP neurons for the LMA circadian rhythm, elucidates organization of circadian outflow from and modulatory input to SCNVIP cells, and demonstrates a subpopulation-level molecular heterogeneity that suggests distinct functions for specific SCNVIP subtypes.
